Imbalanced dataset in machine learning
Data is crucial to train machine learning(ML) models. An ML model is only as good as the data it feeds on. However, data used to train models may have several deformities, for example:
- Missing values and outliers,
- Noisy and inconsistent data,
- Bias resulting from improper sampling,
- Imbalanced data, etc.
In this article, we will focus on the imbalanced dataset, its effect on the resulting model and ways to mitigate the problem.
Imbalanced Dataset
An imbalanced dataset consists of unevenly distributed classes. For example, if you are trying to predict if a tumour is benign or malignant, your dataset is likely to contain way more instances that are benign than are malignant.
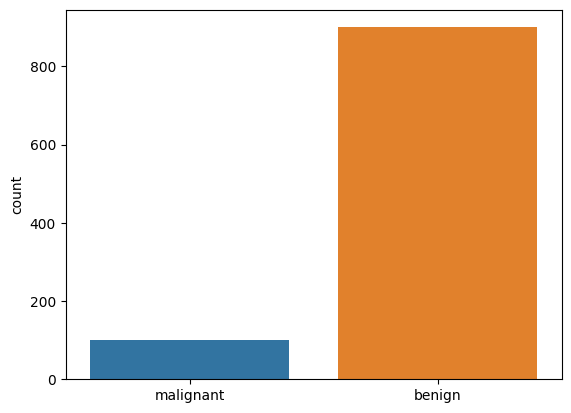
We will discuss the effects of imbalanced dataset in a while but for now let’s focus on the cause of imbalanced datasets. Common causes include:
- Event Rarity: Some events are rare. If we collected data to predict cancer, we will have far more instances of healthy individuals compared to the number of individuals having cancer hence, resulting in imbalanced dataset. Event rarity is common in medical phenomenon, problems related to natural disasters, etc.
- Faulty data collection or sampling: Data collection method also introduce skewness in data. For example, if a company in UK is building an automatic sanitizer dispenser, it is easier for them to collect the data of white individuals than non-white individuals as the number of white people is higher. This results in an imbalanced dataset where non-white people are unevenly represented.
- Data Shift over time: The distribution of available may change over time. For example, if we were collecting data to build a model for COVID detection before 2019, the number of people that were infected by coronavirus would be far less than those who didn’t had any coronavirus infection previously.
Other causes of imbalanced dataset includes legal concerns, instrumental errors, budget constraints, etc.
Effects of imbalanced dataset
An imbalanced dataset is easy to detect. A simple bar/frequency plot can help us identify the problem. However, if left untreated, an imbalanced dataset can become a serious trouble, for both stakeholders and engineers: resulting in legal actions and performance issues.
In 2015, an African-American man at a convention visited the bathroom but the soap dispenser wouldn’t sense his hands. But, when his fellow white friend tried after him, the soap came out immediately. Issues like this can result in a legal action against the company and impair its reputation.
Imbalanced dataset can also be a root cause for numerous performance issues in a machine learning model. Some common ones are:
- Misclassification of minority class: When dealing with imbalanced datasets, the performance of models often suffers concerning the minority class due to its limited representation during training. This exposure disparity towards the majority class can introduce bias into the model’s predictions, resulting in diminished accuracy when it comes to the minority class.
- Decision Threshold Issues: A common pitfall arises from the utilization of default decision thresholds, usually set at 0.5, within various classification algorithms. Within the context of imbalanced datasets, this practice can trigger erroneous predictions. Instances that rightly belong to the minority class might be erroneously classified as part of the majority class, leading to an integrity breach in the predictive process.
- Evaluation Bias: The conventional evaluation measures, accuracy, fall short of capturing the intricacies of imbalanced datasets. While a model might excel in accurately predicting the majority class, its potential shortcomings in addressing the significance of the minority class remain hidden. In such cases, we need to carefully choose from metrics such as precision, recall, F1-score, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC-ROC) for assessment within such intricate scenarios.
Having discussed the causes and potential drawbacks of imbalanced dataset, let’s discuss ways to tackle this issue.
Dealing with Imbalanced Dataset
To ensure that machine learning models treat all classes impartially and make sensible predictions, it is important that we address the issue of class imbalance before training the model. Some effective ways to tackle imbalanced dataset include:
- Resampling(Over and Under sampling): Resampling involves dropping samples from the majority class or increasing samples from the minority class, by duplicating or augmenting, in order to make the class size proportional is called resampling. It is the easiest method to remove class imbalance from the dataset.
- Choosing the right loss function and evaluation metrics: Adjusting the class weight of a loss function such that the model is penalized heavily if it incorrectly classifies a minority class can help improve the model performance. Additionally, as discussed previously, it is better to use metrics like precision, recall, f1 score instead of accuracy to evaluate the model when dealing with imbalanced dataset.
- Ensemble methods: Some algorithms like AdaBoost and XGBoost can handle class imbalance by assigning more weight to misclassified instances. Importantly, algorithms like bagging and random forest combine predictions from multiple uncorrelated models and this helps reduce the bias caused by imbalance in the training dataset.
- Synthetic data generation: Synthetic data generation refers to the creation of artificial samples for minority class with the goal of balancing the dataset. With the advancement in generative AI, we can now generate synthetic data that are very close to the real ones. In the next section, we will explore this technique in detail.
Synthetic Data Generation using SMOTE
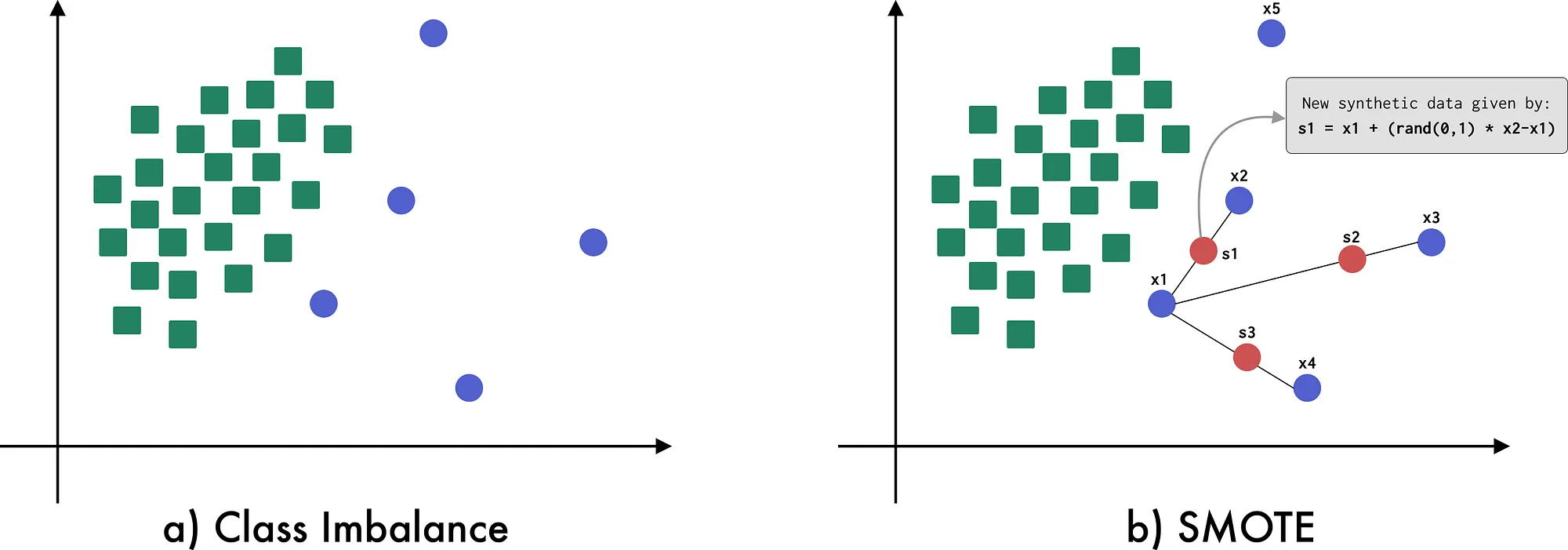
SMOTE, Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique, as the name specifies, is an over-sampling technique for tabular data in which the class imbalance is tackled by generating “synthetic” examples rather than simply over-sampling with replacement.
In SMOTE, the minority class is oversampled by taking an instance of the minority class and then introducing new instances in the line segment joining the instance with its k nearest neighbours. By default the value of k is set to 5, but, depending upon the amount of oversampling required, instances from the k nearest neighbours are chosen randomly. The picture below illustrates the process.
Now, we will use imbalanced-learn, an open source python library, to implement over sampling using SMOTE. We will use a dummy dataset to run our experiment. We recommend that you use google colab to follow the experiment.
- Install imbalanced-learn:
!pip install -U imbalanced-learn - Import necessary modules and libraries:
from collections import Counter
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
- Create a dummy dataset using make_classification
X, y = make_classification(n_classes=2, class_sep=2,
weights=[0.1, 0.9], n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, flip_y=0,
n_features=20, n_clusters_per_class=1, n_samples=1000, random_state=10)
- Check the label distribution in the dummy dataset.
print(Counter(y))
You will find that there is class imbalance in our dataset. Instances with label 1 are way more frequent(900) than instances with label 0, just 100.
- Now, let’s use SMOTE to tackle this issue.
sm = SMOTE(random_state=42)
X_res, y_res = sm.fit_resample(X, y)
Now, if you check the class distribution, you will see that our dataset is balanced. Both classes now have 900 instances each.
print('Balanced dataset shape %s' % Counter(y_res))
Conclusion
Imbalanced dataset is a common issue in machine learning. Left untreated, this can cause serious legal and performance issues. But the good news is, plenty of open source projects like imbalanced-learn and techniques like SMOTE that can be applied to effectively reduce class imbalance from the dataset and prevent associated issues in the final model.
Related Tags:
[imbalanced-dataset machine-learning smote scikit-learn Archive
machine-learning cnn smote self-supervised scikit-learn resnet random-forest rag llms llm large-language-models imbalanced-dataset image-classification ensemble decision-tree computer-vision